Contact Center IVR Solutions
Create smart IVR menus effortlessly
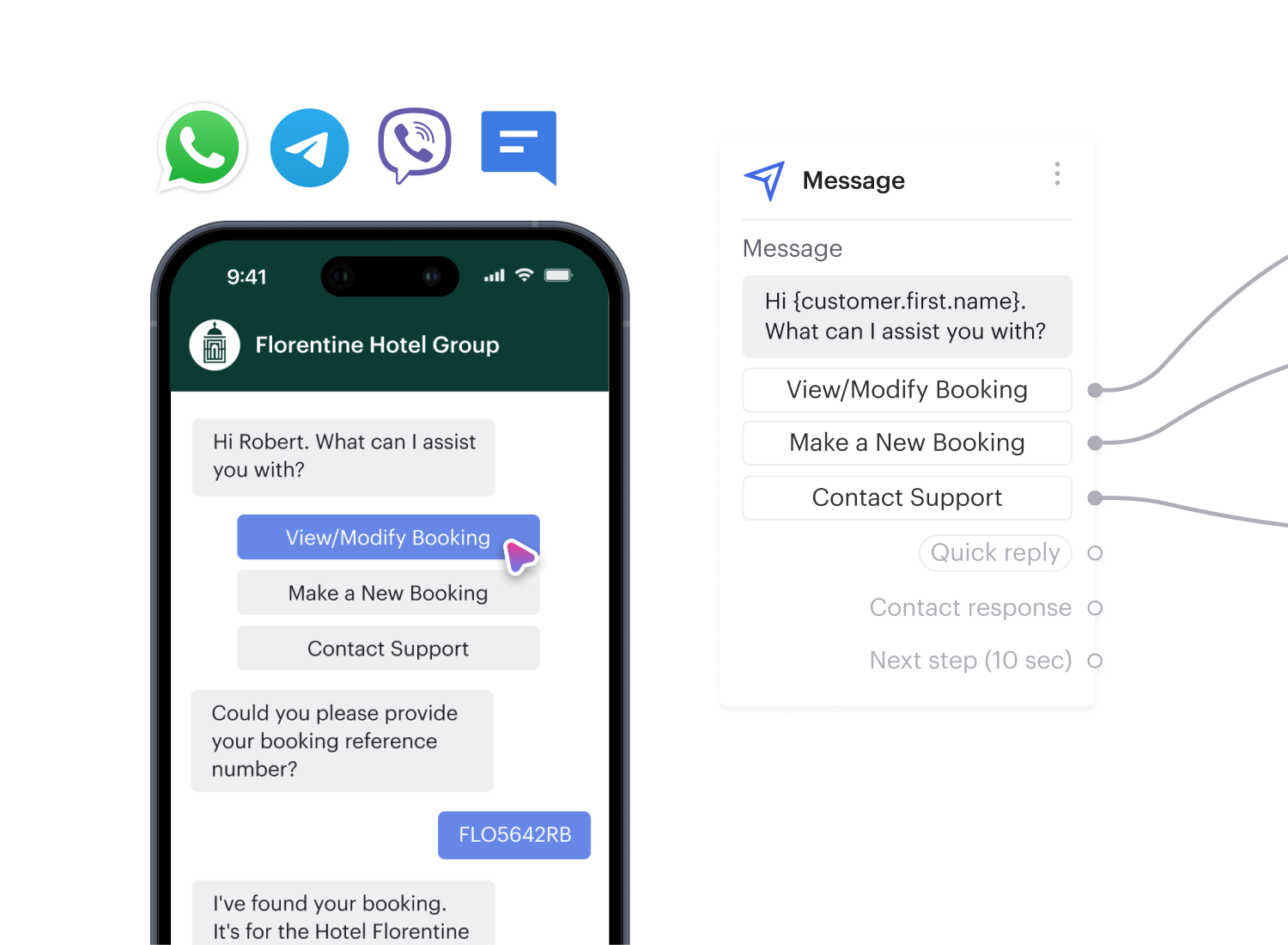
Say goodbye to complex IVR setups. Voiso's Flow Builder lets you design and deploy interactive voice menus in minutes using a single visual tool.


Scale your support the simple way
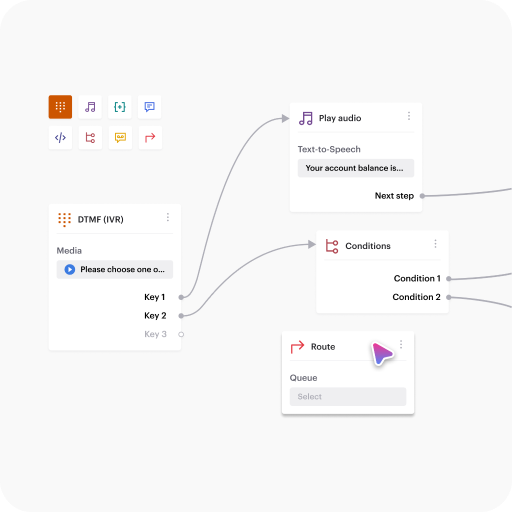
Easy-build IVR
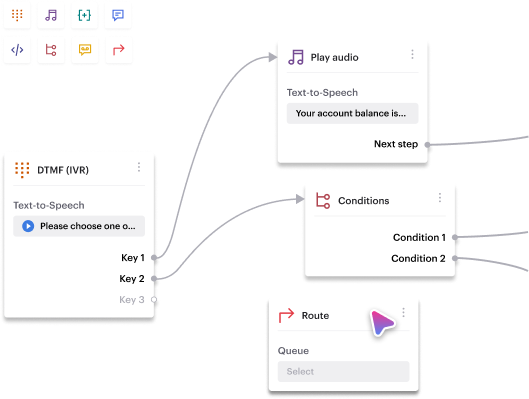
Voiso’s Flow Builder tool allows businesses to create customizable IVR systems that route inbound calls efficiently.
Using a visual interface, users can set up call flows, define actions, enable self-service, and ensure callers reach the right department.
This approach simplifies call handling and improves customer experience by offering tailored responses based on caller input.
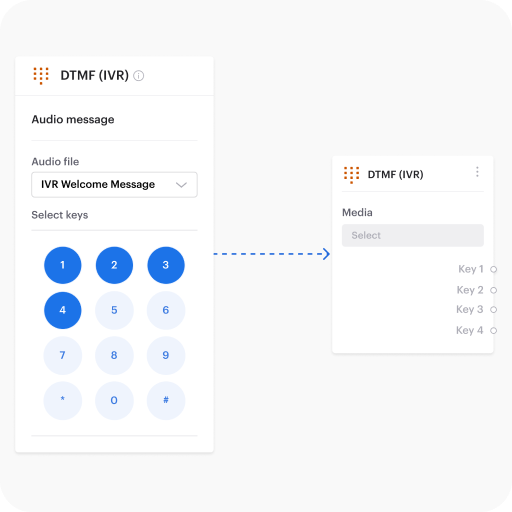
Set up keypad options
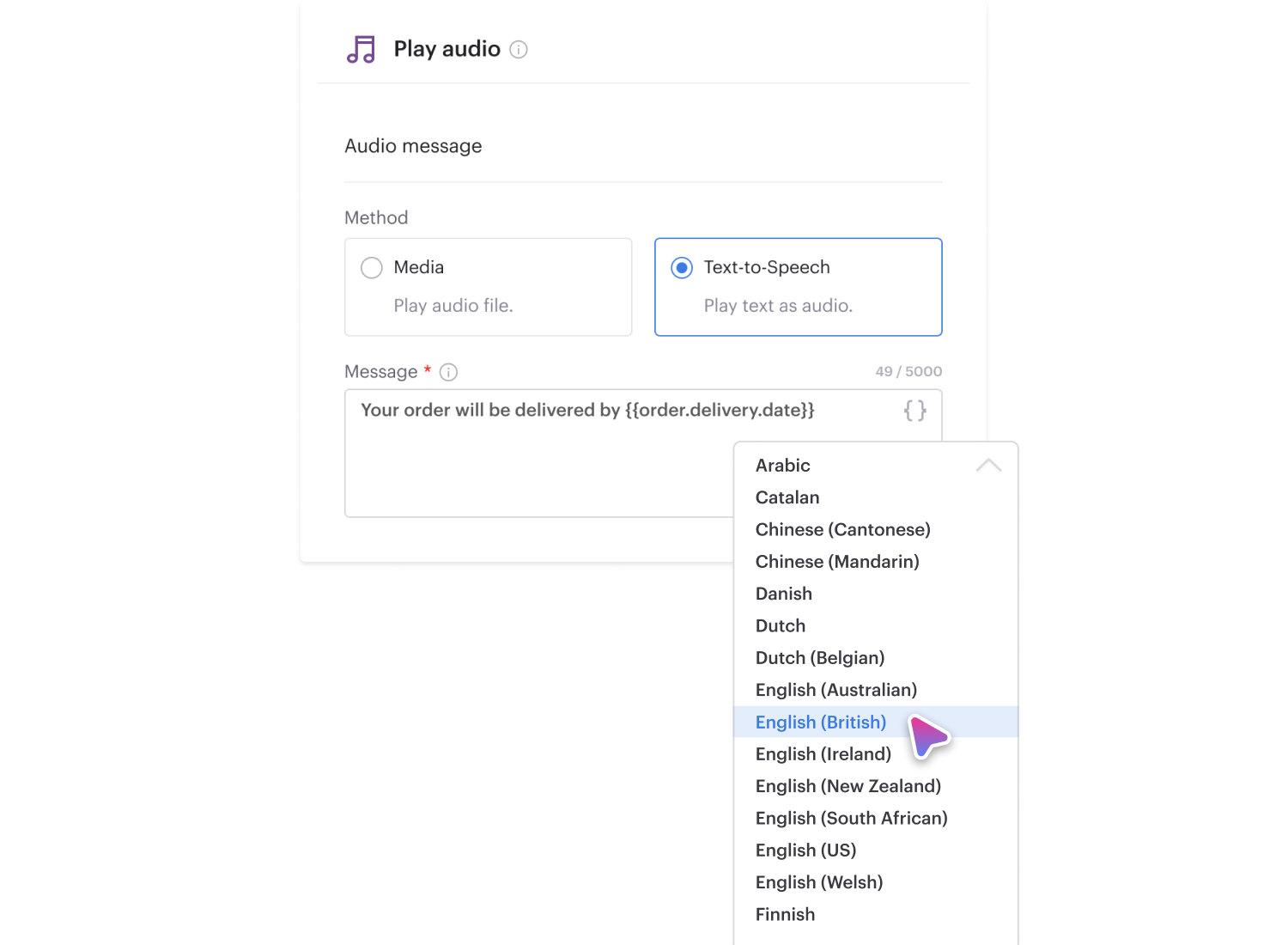
Voiso’s IVR system supports DTMF (Dual Tone Multi Frequency) inputs, enabling callers to interact with automated menus using their phone keypad.
With Flow Builder, you can easily configure number-based actions that route calls or trigger specific responses, streamlining call routing and minimizing wait times for customers.
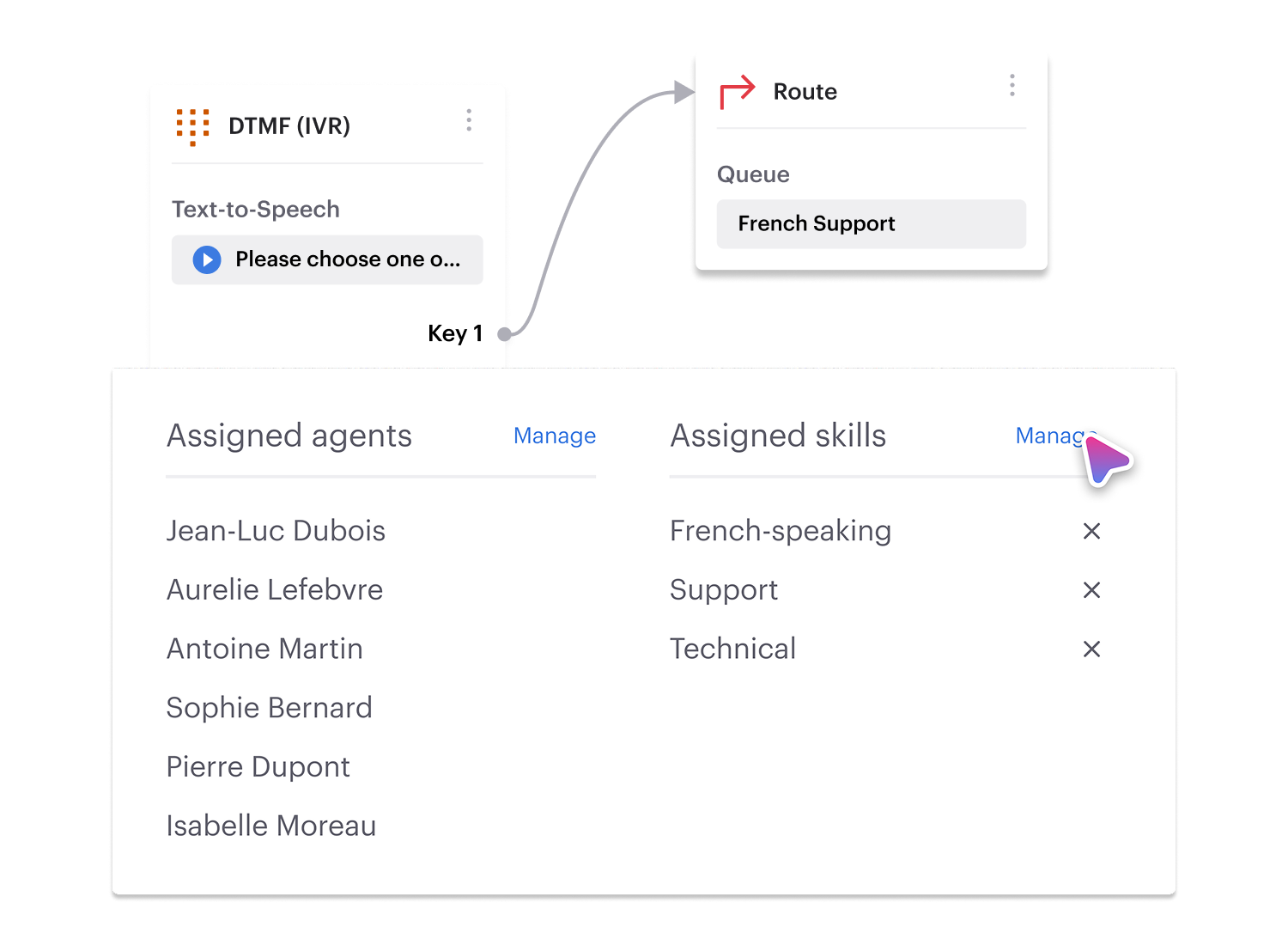
Multi-tiered IVR
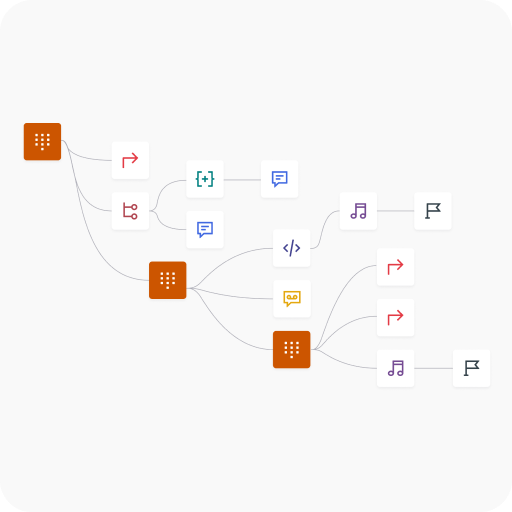
Need a more complex menu?
Voiso’s Flow Builder supports multi-level IVRs, making it easy to add layers of options. Whether you have multiple departments or service tiers, you can ensure every caller finds the right help with ease.
Flow Builder
customers

Get started in less than 24 hours
FAQs on Voiso's IVR system
What is IVR?
IVR stands for Interactive Voice Response. It’s a technology that allows businesses to interact with callers through pre-recorded or text-to-speech voice prompts and menus, and gather responses via keypad inputs or speech recognition. IVR systems can handle a wide range of tasks, from providing information and routing calls to enabling self-service options like bill payments or appointment scheduling.
How does IVR work?
When a caller dials your business number, the IVR system answers the call and presents a series of pre-recorded prompts or menus. The caller can then interact with the system using their phone’s keypad (DTMF tones) or, in some advanced systems, through voice commands. Based on the caller’s input, the IVR system can provide information, route the call to the appropriate agent or department, or enable the caller to complete a self-service task.
What are the benefits of IVR?
IVR offers numerous benefits for businesses, including:
- Improved customer experience: IVR provides 24/7 support, reduces wait times, and enables self-service options, leading to greater customer satisfaction.
- Increased efficiency: IVR automates routine tasks, freeing up agents to focus on more complex issues, improving overall call center efficiency.
- Cost savings: By automating tasks and reducing the need for live agents, IVR can help businesses save on operational costs.
Scalability: IVR systems can easily handle high call volumes and adapt to changing business needs, making them a scalable solution for growing businesses. - Data collection and insights: IVR can collect valuable data about caller interactions, providing insights into customer behavior and preferences.
- Professional image: A well-designed IVR system can project a professional image and enhance your brand reputation.
Can the IVR handle high volumes of simultaneous calls?
Yes, Voiso’s IVR is built to handle high volumes of simultaneous calls with ease. It uses intelligent call routing, automated self-service options, and seamless integration with CRM systems to reduce agent workload and improve customer experience. The system is highly scalable, ensuring consistent performance even during peak call times.
How can I customize the IVR for my business needs?
You can customize Voiso’s IVR using the no-code Flow Builder, which lets you design call flows with a drag-and-drop interface. You can set up custom menus, call routing rules, self-service options, and CRM integrations to match your business needs. It also supports text-to-speech, pre-recorded messages, and multi-level IVR for more advanced automation.
What are the types of IVR?
Voiso supports two main types of IVR:
- Single-Level IVR – A basic menu where callers choose from a set of options (e.g., “Press 1 for Sales, Press 2 for Support”).
- Multi-Level IVR – A more advanced system with multiple layers of menus, allowing for detailed call routing and automation (e.g., “Press 1 for Sales,” then “Press 1 for New Customers, Press 2 for Existing Customers”).
Both types can be customized using Voiso’s Flow Builder for tailored call experiences.
What are the core features of IVR systems?
- Menu Routing
– Present callers with automated prompts (e.g., “Press 1 for Sales”) for self-navigation. - Speech Recognition
– Interpret spoken commands or keywords, reducing reliance on touch-tone input. - Data Integration
– Retrieve or update customer details by connecting with CRMs, databases, or other back-end systems. - Self-Service Transactions
– Let callers perform actions (e.g., check account balance) without agent intervention. - Call Queuing & Routing
– Place callers in queues and direct them to the right agent or department. - Analytics & Reporting
– Track call volumes, menu selections, and drop-offs for optimization insights. - Personalized Prompts
– Customize greetings and messages based on caller ID, language settings, or past interactions.
IVR systems help organizations automate routine inquiries, gather caller data upfront, and efficiently route calls to the right destination, ultimately reducing wait times, lowering operational costs, and enhancing the overall customer experience.
How to set up an IVR system?
- Define Goals & Requirements
– Determine the purpose of the IVR (e.g., self-service options, call routing) and outline the key use cases. - Map Out Call Flows
– Sketch the sequence of prompts and menu options (e.g., “Press 1 for Sales, 2 for Support”).
– Identify any data the IVR needs to collect (e.g., account number, language preference). - Choose Your IVR Platform
– Decide on a solution—cloud-based or on-premises—based on budget, scalability needs, and required integrations. - Configure Integrations
– Connect to CRMs, databases, or other back-end systems for real-time data lookups and updates.
– Ensure all necessary APIs or connectors are set up for information exchange. - Create & Record Prompts
– Record professional audio files or use text-to-speech for each IVR prompt.
– Ensure prompts are concise, clear, and easy for customers to follow. - Set Up Routing & Queues
– Define routing rules (e.g., skill-based routing, time-of-day routing).
– Configure call queues for each department or support team. - Test & Refine
– Run test calls to confirm menu navigation, prompt clarity, data retrieval, and proper call routing.
– Iterate based on agent feedback and real-time analytics. - Deploy & Monitor
– Go live with your IVR configuration, then track metrics like call abandonment, menu selection rates, and customer satisfaction.
– Optimize flows regularly to improve usability and efficiency.
An effective IVR setup streamlines routine inquiries and ensures that callers quickly reach the right destination, ultimately reducing operational costs and enhancing customer satisfaction.
What are the differences between IVR and other call-routing methods?
When designing inbound call strategies, organizations can choose from a variety of methods to direct incoming calls to the right destination. Some opt for a multi-tiered Interactive Voice Response (IVR) system with prompts and self-service options, while others use simpler approaches like direct extensions, skill-based routing, or time-of-day rules. Each method has distinct advantages and drawbacks, often hinging on factors like complexity, caller engagement, and the need for self-service. Understanding these differences helps businesses pick the right solution for their communication needs.
- User Input vs. Automated Distribution
– IVR relies on callers responding to voice prompts or keypad entries. Other methods (e.g., automatic call distribution) can instantly direct calls based on pre-set rules, no input from the caller required. - Self-Service Capabilities
– IVR can let callers solve simple tasks themselves (e.g., check account balances) before talking to an agent. Basic call-routing methods often just connect the caller to a queue or department without self-service options. - Complexity & Customization
– IVR systems can become quite elaborate, supporting multiple tiers of menus, data lookups, and integrations. Simpler routing (like direct extensions or time-of-day routing) has fewer moving parts but offers less flexibility. - Caller Engagement
– IVR actively engages the caller by prompting them to choose from multiple paths. Other routing approaches may be more passive, automatically distributing incoming calls without direct caller interaction. - Integration & Data Access
– IVR often ties into back-end systems to retrieve or update caller data in real time. Basic call-routing methods typically don’t require, or even support, these integrations.
Ultimately, IVR stands out for its interactive and often more sophisticated call-flow design, while other call-routing methods focus on simpler, rule-based delivery of inbound calls.