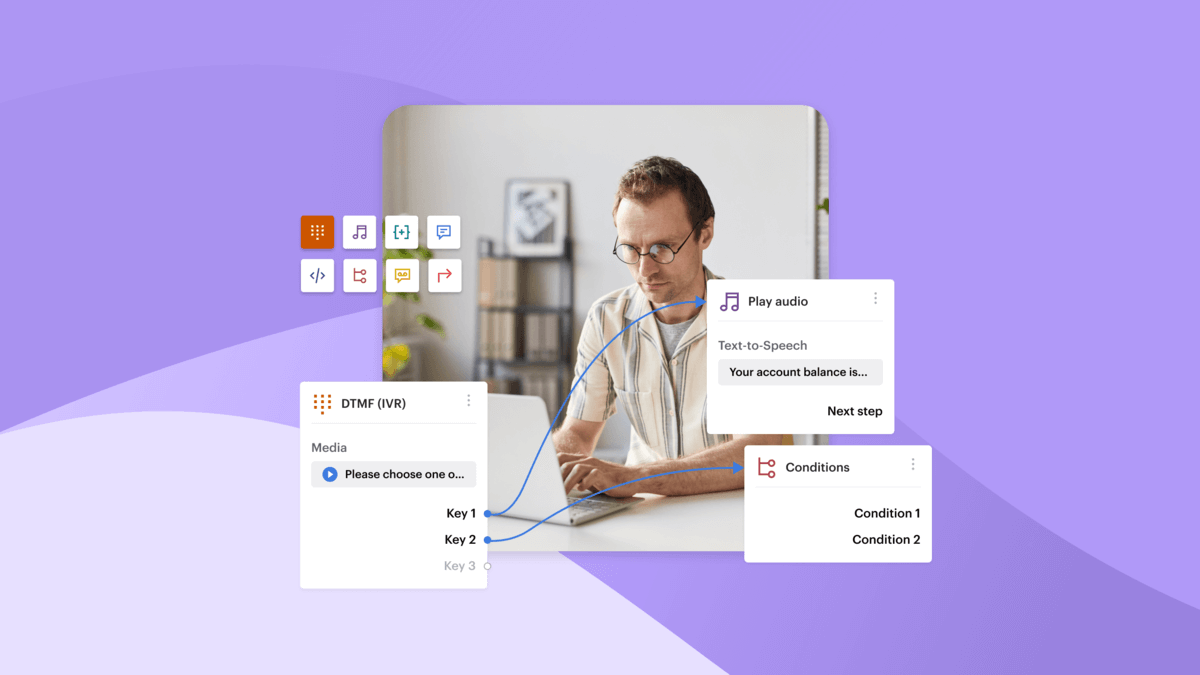
Interactive Voice Response (IVR) systems are the backbone of call center operations. They handle the critical first interaction with customers, manage high call volumes, and determine whether an interaction has been quickly resolved or requires human intervention.
While IVR technology has been around for decades, the landscape has evolved dramatically. Today, there are many types of IVR systems, each designed to meet specific operational needs, customer demands, and business goals.
Takeaways: Different Types of IVR Systems
- IVR diversity meets varied business needs: From simple call routing to advanced AI interactions, IVRs are tailored to operational goals, customer expectations, and technological capabilities.
- Basic & Multi-Level IVR: Keypad-based systems for small or structured operations; multi-level menus handle more complex routing across departments.
- Self-Service IVR: Automates common tasks like account checks, bill payments, or bookings, reducing agent workload and call handling time.
- Dynamic IVR: Personalizes menus based on real-time customer data, enhancing efficiency and customer satisfaction.
- Speech-Enabled & Visual IVR: Natural language interaction or visual menus improve accessibility, speed, and user experience.
- Hosted/Cloud IVR: Offers scalable, low-maintenance solutions for businesses needing flexibility and centralized management.
- AI-Powered IVR: Conversational, intelligent routing that handles complex queries and analyzes sentiment to enhance service.
- Outbound IVR: Automates proactive calls for notifications, confirmations, or feedback collection, freeing agents for complex interactions.
- Hybrid & Omnichannel IVR: Combine automation with live agent support and integrate multiple communication channels for seamless experiences.
- Transactional IVR: Secure handling of payments, account updates, and sensitive transactions with compliance safeguards.
- Multi-Language IVR: Supports diverse customer bases by delivering services in preferred languages, enhancing accessibility.
- Intelligent Call Routing IVR: Uses caller data and agent availability to route calls efficiently, boosting satisfaction and operational efficiency.
- Feedback IVR: Collects post-interaction surveys to measure satisfaction, agent performance, and service quality, enabling continuous improvement.
- Key advantages across IVR types: Reduce agent workload, personalize experiences, improve engagement, ensure scalability, enhance security, and provide actionable insights for optimization.
Why are there so many types of IVR?
IVR isn’t a ‘one-size-fits-all’ solution. . Some businesses prioritize cost savings, and want customers to handle simple requests themselves, while others need advanced AI-driven IVRs to deliver personalized support or handle complex queries. A global contact center might require multi-language IVR, while an outbound campaign needs a system designed for proactive customer engagement.
IVR is evolving in line with customer expectations and technological advancements; the rise of omni-channel communication, AI, and data integration has redefined what IVR can do. IVR can now seamlessly integrate with CRM systems, offer real-time insights, and improve agent efficiency by pre-qualifying calls.
As operational goals shift – whether by reducing handling times, boosting first-call resolution, or ensuring compliance – specialized IVR systems are here to help.
15 Types of IVR
There are multiple IVR types, each with distinct features:
- Basic IVR
- Self-Service IVR
- Multi-Level IVR
- Dynamic IVR
- Speech-Enabled IVR
- Visual IVR
- Hosted/Cloud IVR
- AI-Powered IVR
- Outbound IVR
- Hybrid IVR
- Omni-Channel IVR
- Transactional IVR.
- Multi-Language IVR
- Intelligent Call Routing IVR
- Feedback IVR
Let’s look at the different types of IVR systems and explore why they matter for call centers.
1. Basic IVR
Basic IVR represents the most straightforward approach by relying on pre-recorded messages and simple keypad inputs to route calls. Callers select options from a menu to connect with the right department or service:for example, “Press 1 for Sales” or “Press 2 for Support.”
Use Cases for Basic IVR
- Small contact centers: Often used by businesses with limited call volumes or straightforward routing needs, such as local service providers or small retailers.
- Seasonal campaigns: Ideal for temporary setups like holiday promotions or event registrations where minimal customization is needed.
- Emergency hotlines: Efficient for managing high call volumes during specific crises, offering quick routing to relevant information or departments.
Basic IVR is affordable and easy to set up, and is an excellent starting point for call centers that don’t require advanced capabilities. Regardless, it still lacks certain advanced features, like personalization, integration with CRMs, and the ability to handle complex queries. Plus, callers navigating long menus can quickly become frustrated, leading many modern centers to adopt more flexible or intelligent IVR systems.
2. Self-Service IVR
Self-Service IVR enables customers to resolve common queries independently, without the need for human assistance. Automated menus allow users to access essential services quickly and efficiently, like checking account balances, resetting passwords, or booking tickets.
Use Cases for Self-Service IVR
- Banking and finance: Allows customers to retrieve account details or transaction histories without waiting for an agent.
- Utilities and telecom: Simplifies bill payments, service activations, or troubleshooting guidance.
- Travel and hospitality: Facilitates booking or rescheduling tickets and checking reservation statuses.
The appeal of Self-Service IVR lies in its efficiency:it reduces agent workload, shortens call handling times, and is capable of operating 24/7, unlike human agents. Customers appreciate the autonomy it offers for simple tasks, but poorly designed menus can frustrate users, leading them to live support agents instead. Plus, while it’s excellent for straightforward queries, it may not suit scenarios that need personalized assistance or complex decision-making.
3. Multi-Level IVR
Multi-Level IVR builds on the simplicity of basic IVR with layered menus, making it ideal for businesses with multiple service levels. Instead of a single menu, callers navigate through tiers to reach specific departments or services. For example, after selecting “Press 1 for Support,” users might encounter a second menu with options for technical or billing inquiries.
Use Cases for Multi-Level IVR
- Healthcare providers: Directs patients to billing, appointment scheduling, or specific medical departments.
- E-commerce and retail: Guides customers through inquiries about orders, returns, or product-specific support.
- Telecommunications: Handles various requests, from troubleshooting to account upgrades, through segmented pathways.
Multi-level IVR is capable of managing multiple caller needs efficiently with precise routing, reducing the chances of misdirected calls, which ultimately saves agents’ time. For businesses handling a wide range of services or large call volumes, this structure is priceless.
But remember to prioritize user-friendliness: too many memu layers can overwhelm customers, leading to frustration and higher abandonment rates. Regularly reviewing menu effectiveness is essential in understanding how customers are experiencing the IVR system.
4. Dynamic IVR
Dynamic IVR is a huge step up from traditional IVR menus: it personalizes call flows based on real-time data using information like customer history, account status, or past interactions to tailor menus and options to the caller’s specific needs. Instead of offering generic options, Dynamic IVR anticipates user requirements, streamlining the experience.
Use Cases for Dynamic IVR
- Financial services: Automatically provides account balances or recent transactions to authenticated callers.
- E-commerce: Offers updates on recent orders or prioritizes routing for premium customers.
- Utilities: Suggests relevant options, such as reporting outages, based on the caller’s geographic location.
Dynamic IVR significantly reduces manual effort, leading to better overall customer satisfaction. Since callers don’t have to navigate through irrelevant options, they experience more efficient, less frustrating calls. Businesses can benefit from a better brand image and optimized efficiency, especially when dealing with high-value clients, while customers can be supported quicker and easier.
Despite its obvious benefits, dynamic IVR implementation requires robust integration with CRMs or databases to access and process user data effectively. Without it, Dynamic IVR can’t deliver the personalized experience it promises.
5. Speech-Enabled IVR
Speech-Enabled IVR leverages advanced speech recognition technology to allow callers to interact using natural language instead of keypad inputs, creating a faster, more intuitive experience. Callers can simply state their request, such as “Check my account balance” or “Transfer me to technical support,” to progress through the system.
Use Cases for Speech-Enabled IVR
- Healthcare: Patients can say “Schedule an appointment” or “Talk to billing” to reach the correct department without pressing multiple keys.
- Travel and hospitality: Handles spoken requests for booking details, flight status, or hotel check-ins.
- Government services: Simplifies access to information about taxes, benefits, or permits through voice prompts.
Speech-Enabled IVR’s benefit is accessibility and convenience by catering to users who may have difficulty navigating menus, such as those unfamiliar with technical systems or those with disabilities.
Accurate voice recognition, while highly useful, relies heavily on clear audio input and advanced language models. Background noise, accents, or ambiguous phrasing can lead to errors, which can sometimes lead to frustrated callers having to repeat themselves.
6. Visual IVR
Visual IVR reimagines traditional call menus by integrating a visual interface that users can access on their smartphones, websites, or mobile apps. Instead of listening to menu options, callers view and interact with them directly, making navigation faster and more intuitive.
Use Cases for Visual IVR
- Retail and e-commerce: Customers can visually browse options for order tracking, product returns, or support categories.
- Healthcare: Patients schedule appointments or view prescription refill options with easy-to-understand visual prompts.
- Travel and hospitality: Travelers access flight updates, check-in options, or booking modifications in an interactive format.
The visual format significantly reduces frustration by allowing users to select options at their own pace. It also shortens resolution times by offering direct access to rich media, such as forms, videos, or maps, for additional guidance.
On the other hand, Visual IVR requires strong integration with mobile-friendly platforms, which means it may not suit every demographic. Users without smartphones or those unfamiliar with digital interfaces might find it inaccessible. But for call centers targeting a tech-savvy audience or offering visually complex services, Visual IVR can be a game-changer.
7. Hosted/Cloud IVR
Hosted or Cloud IVR leverages cloud-based infrastructure to manage interactive voice response systems. It reduces operational complexity and upfront costs by removing the need for on-premises hardware, meaning call centers can deploy, update, and scale their IVR systems quickly without extensive IT resources.
Use Cases for Hosted/Cloud IVR
- Startups and growing businesses: Scales effortlessly to handle increasing call volumes as the business expands.
- Seasonal operations: Supports temporary campaigns or surges in demand without requiring permanent infrastructure.
- Global contact centers: Connects teams across regions with centralized management and standardized IVR systems.
The flexibility of Hosted/Cloud IVR makes it a popular choice for businesses seeking agility. Updates are instantaneous, and new features are easier to integrate. Cloud-based systems are also more reliable as they typically include disaster recovery and uptime guarantees from providers.
But relying heavily on stable internet connections and third-party services can be a drawback for some call centers. Plus, concerns about data security or compliance with industry regulations might lead certain businesses to consider on-premises alternatives.
8. AI-Powered IVR
AI-Powered IVR revolutionizes traditional call handling by incorporating Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Natural Language Processing (NLP). Instead of relying on rigid menus, callers engage in natural, conversational interactions that feel more human and personal. AI-powered IVR analyzes intent, emotion, and language patterns to provide precise responses and route calls intelligently.
Use Cases for AI-Powered IVR
- Customer support: Resolves complex queries like troubleshooting or account issues through interactive conversations.
- E-Commerce: Recommends products or services based on caller intent and browsing history.
- Healthcare: Schedules appointments or provides tailored advice using patient-specific data.
AI-Powered IVR delivers faster, more accurate responses, while intelligently routing callers to the best-suited agents for their queries. It saves time for both customers and agents, significantly improves customer satisfaction, and even reduces employee burnout. Plus, features like sentiment analysis enable real-time adjustments, such as escalating dissatisfied callers to supervisors, to prevent major issues before they have a chance to take root.
Its main downside is the significant investment and robust data infrastructure requirements for implementation, as any misinterpretation of intent or language can lead to frustration, especially for non-standard dialects or complex issues.
9. Outbound IVR
Outbound IVR automates outgoing calls to deliver important information, reminders, or collect feedback. It helps businesses stay ahead of schedules by initiating contact with customers, maintaining engagement, and streamlining operations without tying up agents.
Use Cases for Outbound IVR
- Appointment confirmations: Reminds patients or clients of upcoming appointments and allows them to confirm or reschedule.
- Delivery notifications: Updates customers on delivery statuses, such as shipment dispatch or delays.
- Surveys and feedback: Collects post-interaction feedback or conducts market research efficiently.
Outbound IVR excels in automating repetitive outreach tasks, freeing agents to focus on complex interactions. It also ensures consistent messaging and can handle high call volumes, making it a cost-effective tool for customer engagement. Features like interactive responses also add value by allowing customers to take immediate action, such as confirming an appointment.
Outbound agents may face challenges like low answer rates or regulatory compliance around automated messaging, while overuse can lead to customer annoyance, damaging brand perception.
10. Hybrid IVR
Hybrid IVR combines the efficiency of call center automation with the expertise of live agents, creating a balanced approach to customer interaction. It enables customers to complete straightforward tasks through self-service, seamlessly transitioning them to human agents when the issue requires personalized support or complex resolution.
Use Cases for Hybrid IVR
- Technical support: Automates troubleshooting for common issues and connects customers to agents for advanced problems.
- Banking: Allows users to check balances or recent transactions and transfer to an agent for loan inquiries or account disputes.
- Healthcare: Handles appointment bookings through IVR while escalating medical-specific concerns to a representative.
Hybrid IVR is highly flexible: It automates routine tasks often relying on ACD systems, reduces agent workload and wait times, and ensures customers feel supported by transferring them to human agents as needed, ultimately improving satisfaction and first-call resolution.
Any delays or interruptions during handoffs can frustrate callers, though, which means implementing a Hybrid IVR requires a thoughtful balance between automation and human interaction to ensure smooth transitions and effective resource allocation.
11. Omnichannel IVR
OmniChannel IVR integrates traditional phone-based systems with multiple communication channels like SMS, messaging apps, and web chat. It allows customers to start an interaction on one platform and seamlessly transition to another while maintaining context and continuity, ensuring a consistent and cohesive experience, regardless of the channel a customer chooses.
Use Cases for Omnichannel IVR
- E-commerce: Enables customers to inquire about a product via chat, confirm an order through IVR, and receive delivery updates via SMS.
- Customer support: Allows users to escalate a web chat inquiry to a phone call without losing conversation history.
- Travel and hospitality: Supports booking modifications started via IVR and completed through email confirmation.
Omnichannel IVR improves customer experience by providing flexibility and continuity. Customers can choose their preferred communication method and switch platforms as needed, boosting operational efficiency by unifying data across communication channels andgiving agents a complete view of customer interactions.
Implementing Omnichannel IVR requires strong integration between systems and a centralized data infrastructure, without which, inconsistencies and data silos may arise, undermining its effectiveness.
12. Transactional IVR
Transactional IVR is specifically designed to handle secure processes such as bill payments, account updates, and ticket purchases. By integrating advanced security measures, it ensures sensitive data like payment details or account credentials remain protected while customers complete their tasks.
Use Cases for Transactional IVR
- Banking and finance: Securely facilitates loan payments, balance transfers, and account updates.
- Utilities: Enables customers to pay bills, check account statuses, or report outages without agent involvement.
- Travel: Handles ticket bookings, upgrades, and cancellations with real-time confirmation.
The primary benefit of Transactional IVR is its ability to efficiently process secure transactions, reducing the risk of human error, ensuring compliance with data protection standards like PCI DSS, and lowering costs by automating repetitive payment or update tasks.
But, Transactional IVR implementation requires significant investment in encryption and data protection technology. Poorly executed systems can lead to security vulnerabilities or customer mistrust, which is especially important for call centers handling frequent financial or sensitive interactions, Transactional IVR can be highly beneficial, provided it meets the highest security standards and delivers a seamless user experience.
13. Multi-Language IVR
Multi-Language IVR offers menu navigation and responses in multiple languages, making it a vital tool for businesses with a diverse or global customer base. It provides more personalized experiences by recognizing a caller’s location or language preference,, improving clarity and engagement.
Use Cases for Multi-Language IVR
- Global e-commerce: Provides support in the customer’s native language for inquiries and order tracking.
- Healthcare providers: Assists patients with appointment scheduling or information in their preferred language.
- Travel and tourism: Enables international travelers to access services in multiple languages, such as flight information or booking support.
For businesses serving multicultural or international audiences, Multi-Language IVR enhances accessibility and customer satisfaction. It reduces language barriers, enabling clear communication and faster resolutions, but can come with some disadvantages, such as more complex setup, ongoing translation updates, and cultural nuances.
14. Intelligent Call Routing IVR
Intelligent Call Routing IVR takes customer interactions beyond basic menus by analyzing caller data, agent availability, or priority levels to direct calls efficiently. Instead of routing calls randomly or sequentially, it ensures that each caller is connected to the most suitable agent or department based on predefined criteria.
Use Cases for Intelligent Call Routing IVR
- Customer support: Prioritizes VIP customers or escalated issues to senior agents for faster resolutions.
- Sales: Routes calls to specific agents based on regional expertise, product knowledge, or language skills.
- Healthcare: Directs patients to the right specialist or service based on their medical history or query type.
Intelligent call routing IVR improves both customer satisfaction and operational efficiency by reducing wait times and ensuring that callers are matched with the most qualified agents. It optimizes resource allocation, helping call centers manage high call volumes more effectively.
Intelligent Call Routing requires integration with databases and workforce management tools to access real-time information, so call centers without the necessary data infrastructure may struggle to implement it fully.
15. Feedback IVR
Feedback IVR automates the process of collecting customer opinions and ratings after interactions. By seamlessly engaging callers at the end of a service call, it provides valuable insights into customer satisfaction, agent performance, and service quality.
Use Cases for Feedback IVR
- Customer support: Collects ratings on agent professionalism, issue resolution, and overall satisfaction.
- Retail and e-commerce: Gathers opinions on recent purchases, delivery experiences, or returns processes.
- Utilities and telecom: Tracks feedback on outage handling, billing inquiries, or technical support.
Feedback IVR is a cost-effective way to gather actionable data without requiring additional staff. It provides real-time insights that help call centers identify service gaps and drive continuous improvement, while customizable survey options allow businesses to focus on metrics most relevant to their goals.
But overuse or poorly designed surveys can sometimes annoy customers and lead to low participation rates. Call centers must ensure that surveys are concise, relevant, and introduced appropriately.
Key Takeaways
- IVR diversity reflects business needs: Different IVR types address varied operational challenges, from simple call routing to advanced conversational AI.
- Efficiency and personalization: Systems like Self-Service and AI-Powered IVR reduce agent workload while delivering tailored experiences.
- Enhanced customer engagement: Options like OmniChannel and Visual IVR cater to modern, tech-savvy customers across multiple platforms.
- Scalability and security: Hosted/Cloud and Transactional IVR ensure flexible operations and secure transactions for call centers.
- Data-driven improvements: Feedback and Intelligent Call Routing IVRs provide actionable insights and ensure resource optimization.
Further Reading